S汽车零件公司生产性物料采购成本管理优化探讨
时间:2025-06-13 来源:www.51mbalunwen.com
本文是一篇生产管理论文,笔者通过对S公司的生产性物料采购成本的分析研究,为公司的采购成本管理优化策略提供了科学的依据,这些策略不仅有助于S公司在激烈的市场竞争中实现利润的增长和可持续发展,也为其他汽车零部件制造企业提供了降低生产性物料成本的参考和借鉴。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background and Significance
1.1.1 Research Background
In the wave of globalization, the automobile has established its status as one of the most widely used modes of transportation worldwide. The automotive industry is a highly diversified and complex field, encompassing not only vehicle manufacturing but also parts production, engine manufacturing, and various other subfields. China, with its vast automobile consumption market and steady growth in national income, has seen a continuous increase in automobile production and sales, making cars an extremely common mode of transport among Chinese families. As of June 2024, the total number of automobiles in China has risen to 345 million, with new energy vehicles emerging as a significant force in the automotive sector, boasting a total ownership of 24.72 million units. Furthermore, in just the first half of 2024, the number of newly registered new energy vehicles reached 4.397 million, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 39.41%. This figure not only underscores the rapid development of the automotive industry but also indicates that the sector is undergoing an unprecedented transformation, presenting unprecedented challenges and pressures for traditional automotive companies, forcing them to adapt to this new market dynamic.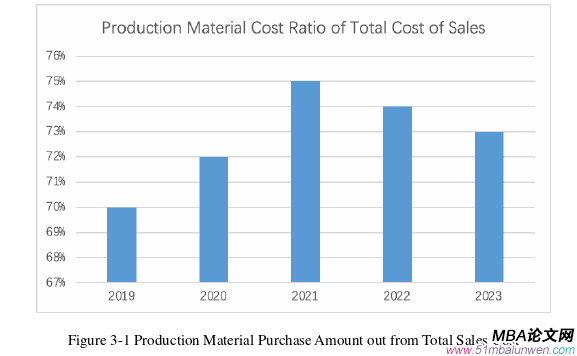
生产管理论文怎么写
....................
1.2 Research Questions and Objectives
1.2.1 Research Questions
In a highly competitive market environment, the management and optimization of purchasing costs have become key to enhancing a company's competitiveness. Research studies have shown that the proportion of production purchasing costs in S Company's total costs exceeds 70%. Therefore, how to optimize the purchasing costs of production materials is an important strategy for S Company to improve profits and market competitiveness. This paper will systematically use methods such as literature review, research investigation, and case study to discover that as an international enterprise, S Company has comprehensive and stable operational management mechanisms, such as purchasing management, design and development management, and quality management. S Company overemphasizes the importance of compliance with processes and standards, neglecting the high purchasing costs that come with it, reducing the flexibility and competitiveness in adapting to market development. This paper identifies the core issues in S Company's management of production material purchasing costs, which are specifically manifested in the following three points:
(1) High Explicit Costs: S Company's design and R&D centers are spread across the world, and the selection of raw materials and process standards are determined based on the location of the R&D centers. Due to the different regions of the design centers, the raw materials used also vary. This global design and manufacturing in China leads to a dispersed selection of raw materials, resulting in a high variety of materials but low quantities, thereby causing high raw material purchasing costs.
(2) High implicit Costs: S Company has a well-established system for supplier management, emphasizing cross-functional management of suppliers. Consequently, each function has imposed strict standards and hefty penalty requirements on supplier management, particularly regarding additional quality costs. These practices have resulted in high implicit costs.
.................................
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Definition of key Concepts
(1) Purchasing of Production material
Purchasing of production material is a critical aspect of enterprise operations management, involving a series of complex activities aimed at achieving production objectives. Specifically, it refers to the process by which an enterprise acquires raw materials, key components, auxiliary materials, and other related items that are directly used in the production process through market transaction mechanisms. This process encompasses multiple stages, including supplier selection, price negotiation, contract signing, order execution, logistics coordination, and inventory management.
The purchasing of production material is not only a basic logistics activity but also a core component of supply chain management. It is directly related to whether an enterprise can efficiently transform raw materials and components into final products to meet market demands. In this process, the enterprise must consider various factors, such as market demand fluctuations, uncertainties in the supply market, cost control pressures, and the stability of the supply chain, to ensure the timely supply and optimal allocation of production material.
..........................
2.2 Overarching Theories
2.2.1 TCO Theory
TCO, or Total Cost of Ownership, refers to the overall costs incurred over the entire lifecycle of an asset or service, and it originated in the 1980s and 1990s. In the mid-1990s, the European logistics industry adopted the TCO approach to calculate the total expenses associated with purchasing vehicles and using them for logistics transportation. Trusaji (2018) argued that purchasing activities also generate indirect and potential costs, which should be included in the consideration of purchasing costs.
TCO, as a practical theory guiding purchasing activities, aims to minimize costs over the full lifecycle of equipment or services. This approach not only focuses on minimizing the upfront costs of hardware but also includes subsequent maintenance, value-added services, and operating expenses. In 1993, the foreign scholar Lisa M. Ellram suggested that the lifecycle of a product or service should at least encompass the stages of acquisition, receipt, ownership, usage, and disposal. Therefore, from the perspective of TCO theory, the associated costs should cover the pre-purchasing, during-purchasing, and post-purchasing phases.
.........................
Chapter 3 Overview of Company S and Current Purchasing Cost Management .................... 24
3.1 Overview of Company S .............................................. 24
3.2 Overview on S Company’s Purchasing Department .................... 28
Chapter 4 Analysis of Issues in Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at Company S........................... 49
4.1 Main Issues Identified ........................ 49
4.1.1 High Explicit Costs .......................................... 51
4.1.2 High Implicit Costs .......................... 52
Chapter 5 Optimization Strategies for Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at S Company ................ 60
5.1 Optimization Objectives and Principles ......................... 60
5.2 Optimization Strategies ................................ 61
Chapter 5 Optimization Strategies for Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at S Company
5.1 Optimization Objectives and Principles
(1) Optimize the VA/VE Process
Improve S Company's current purchasing situation of "multiple varieties, small quantities" by validating equivalent local materials through VA/VE (Value Analysis/Value Engineering) to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and maintain product performance. The goal of this study is to establish a well-defined VA/VE management process, provide economic support for VA/VE activities, and allocate human resources to ensure that the necessary resources are available for the successful implementation of VA/VE. This will help S Company optimize the purchasing costs of production material.
(2) Establish a Pricing Model
In the current rapidly changing market environment, S Company faces increasingly complex pricing challenges. This study aims to establish a dynamic pricing model based on big data analysis that can respond to market changes in real-time and provide scientific costing.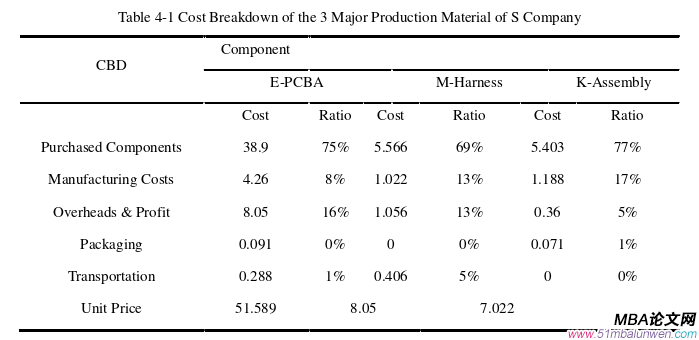
生产管理论文参考
.........................
Chapter 6 Conlusions, Implications and Limitations
6.1 Conclusions
This study is conducted against the backdrop of intensified competition in the automotive manufacturing industry and a slowdown in economic growth, which has become an inevitable choice for various enterprises. Using S Company, an automotive parts manufacturing company, as a case study, the research employs methods such as literature review, surveys, and case studies to explore and comprehensively assess the purchasing cost management issues it faces. The research delves into a detailed analysis of the root causes of these problems. Subsequently, guided by professional theories such as supply chain management theory and TCO theory, and drawing on the experiences summarized from the literature review, systematic and targeted optimization strategies are proposed.
Through this research, the following conclusions are drawn: (1) With the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry and the continuous advancement of autonomous driving technology, transformation and innovation have become inevitable trends for traditional car manufacturers. For automotive parts manufacturing companies, on the one hand, they need to continuously innovate while meeting the market’s high demands for quality. On the other hand, they must reduce costs in the context of a slowing economy, striving for both survival and growth. Therefore, optimizing purchasing cost management has become a common challenge faced by many manufacturing companies.
(2) For S Company, the current purchasing cost management issues include high explicit costs, high implicit costs, and a high supplier homogeneity. The causes of these problems are complex and interconnected with the symptoms, which can be broadly summarized as follows: inappropriate selection of raw materials, lack of a reasonable market pricing mechanism, weak cost-oriented awareness, and overly stringent standards for introducing new suppliers.
reference(omitted)
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background and Significance
1.1.1 Research Background
In the wave of globalization, the automobile has established its status as one of the most widely used modes of transportation worldwide. The automotive industry is a highly diversified and complex field, encompassing not only vehicle manufacturing but also parts production, engine manufacturing, and various other subfields. China, with its vast automobile consumption market and steady growth in national income, has seen a continuous increase in automobile production and sales, making cars an extremely common mode of transport among Chinese families. As of June 2024, the total number of automobiles in China has risen to 345 million, with new energy vehicles emerging as a significant force in the automotive sector, boasting a total ownership of 24.72 million units. Furthermore, in just the first half of 2024, the number of newly registered new energy vehicles reached 4.397 million, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 39.41%. This figure not only underscores the rapid development of the automotive industry but also indicates that the sector is undergoing an unprecedented transformation, presenting unprecedented challenges and pressures for traditional automotive companies, forcing them to adapt to this new market dynamic.

生产管理论文怎么写
1.2 Research Questions and Objectives
1.2.1 Research Questions
In a highly competitive market environment, the management and optimization of purchasing costs have become key to enhancing a company's competitiveness. Research studies have shown that the proportion of production purchasing costs in S Company's total costs exceeds 70%. Therefore, how to optimize the purchasing costs of production materials is an important strategy for S Company to improve profits and market competitiveness. This paper will systematically use methods such as literature review, research investigation, and case study to discover that as an international enterprise, S Company has comprehensive and stable operational management mechanisms, such as purchasing management, design and development management, and quality management. S Company overemphasizes the importance of compliance with processes and standards, neglecting the high purchasing costs that come with it, reducing the flexibility and competitiveness in adapting to market development. This paper identifies the core issues in S Company's management of production material purchasing costs, which are specifically manifested in the following three points:
(1) High Explicit Costs: S Company's design and R&D centers are spread across the world, and the selection of raw materials and process standards are determined based on the location of the R&D centers. Due to the different regions of the design centers, the raw materials used also vary. This global design and manufacturing in China leads to a dispersed selection of raw materials, resulting in a high variety of materials but low quantities, thereby causing high raw material purchasing costs.
(2) High implicit Costs: S Company has a well-established system for supplier management, emphasizing cross-functional management of suppliers. Consequently, each function has imposed strict standards and hefty penalty requirements on supplier management, particularly regarding additional quality costs. These practices have resulted in high implicit costs.
.................................
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Definition of key Concepts
(1) Purchasing of Production material
Purchasing of production material is a critical aspect of enterprise operations management, involving a series of complex activities aimed at achieving production objectives. Specifically, it refers to the process by which an enterprise acquires raw materials, key components, auxiliary materials, and other related items that are directly used in the production process through market transaction mechanisms. This process encompasses multiple stages, including supplier selection, price negotiation, contract signing, order execution, logistics coordination, and inventory management.
The purchasing of production material is not only a basic logistics activity but also a core component of supply chain management. It is directly related to whether an enterprise can efficiently transform raw materials and components into final products to meet market demands. In this process, the enterprise must consider various factors, such as market demand fluctuations, uncertainties in the supply market, cost control pressures, and the stability of the supply chain, to ensure the timely supply and optimal allocation of production material.
..........................
2.2 Overarching Theories
2.2.1 TCO Theory
TCO, or Total Cost of Ownership, refers to the overall costs incurred over the entire lifecycle of an asset or service, and it originated in the 1980s and 1990s. In the mid-1990s, the European logistics industry adopted the TCO approach to calculate the total expenses associated with purchasing vehicles and using them for logistics transportation. Trusaji (2018) argued that purchasing activities also generate indirect and potential costs, which should be included in the consideration of purchasing costs.
TCO, as a practical theory guiding purchasing activities, aims to minimize costs over the full lifecycle of equipment or services. This approach not only focuses on minimizing the upfront costs of hardware but also includes subsequent maintenance, value-added services, and operating expenses. In 1993, the foreign scholar Lisa M. Ellram suggested that the lifecycle of a product or service should at least encompass the stages of acquisition, receipt, ownership, usage, and disposal. Therefore, from the perspective of TCO theory, the associated costs should cover the pre-purchasing, during-purchasing, and post-purchasing phases.
.........................
Chapter 3 Overview of Company S and Current Purchasing Cost Management .................... 24
3.1 Overview of Company S .............................................. 24
3.2 Overview on S Company’s Purchasing Department .................... 28
Chapter 4 Analysis of Issues in Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at Company S........................... 49
4.1 Main Issues Identified ........................ 49
4.1.1 High Explicit Costs .......................................... 51
4.1.2 High Implicit Costs .......................... 52
Chapter 5 Optimization Strategies for Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at S Company ................ 60
5.1 Optimization Objectives and Principles ......................... 60
5.2 Optimization Strategies ................................ 61
Chapter 5 Optimization Strategies for Production Material Purchasing Cost Management at S Company
5.1 Optimization Objectives and Principles
(1) Optimize the VA/VE Process
Improve S Company's current purchasing situation of "multiple varieties, small quantities" by validating equivalent local materials through VA/VE (Value Analysis/Value Engineering) to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and maintain product performance. The goal of this study is to establish a well-defined VA/VE management process, provide economic support for VA/VE activities, and allocate human resources to ensure that the necessary resources are available for the successful implementation of VA/VE. This will help S Company optimize the purchasing costs of production material.
(2) Establish a Pricing Model
In the current rapidly changing market environment, S Company faces increasingly complex pricing challenges. This study aims to establish a dynamic pricing model based on big data analysis that can respond to market changes in real-time and provide scientific costing.

生产管理论文参考
Chapter 6 Conlusions, Implications and Limitations
6.1 Conclusions
This study is conducted against the backdrop of intensified competition in the automotive manufacturing industry and a slowdown in economic growth, which has become an inevitable choice for various enterprises. Using S Company, an automotive parts manufacturing company, as a case study, the research employs methods such as literature review, surveys, and case studies to explore and comprehensively assess the purchasing cost management issues it faces. The research delves into a detailed analysis of the root causes of these problems. Subsequently, guided by professional theories such as supply chain management theory and TCO theory, and drawing on the experiences summarized from the literature review, systematic and targeted optimization strategies are proposed.
Through this research, the following conclusions are drawn: (1) With the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry and the continuous advancement of autonomous driving technology, transformation and innovation have become inevitable trends for traditional car manufacturers. For automotive parts manufacturing companies, on the one hand, they need to continuously innovate while meeting the market’s high demands for quality. On the other hand, they must reduce costs in the context of a slowing economy, striving for both survival and growth. Therefore, optimizing purchasing cost management has become a common challenge faced by many manufacturing companies.
(2) For S Company, the current purchasing cost management issues include high explicit costs, high implicit costs, and a high supplier homogeneity. The causes of these problems are complex and interconnected with the symptoms, which can be broadly summarized as follows: inappropriate selection of raw materials, lack of a reasonable market pricing mechanism, weak cost-oriented awareness, and overly stringent standards for introducing new suppliers.
reference(omitted)
相关阅读
暂无数据


