中国对阿富汗投资的影响因素分析:时间序列分析的视角
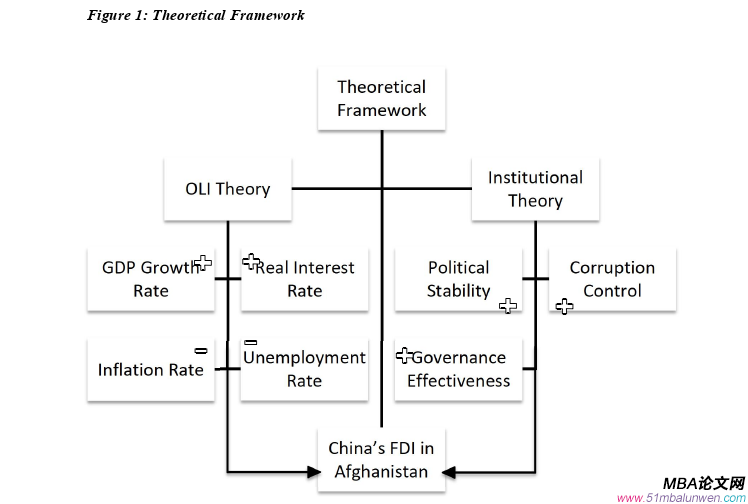
本文是一篇投资分析论文,本论文采用自回归分布滞后(ARDL)模型分析数据,探讨了各种经济和政治因素之间的动态相互作用及其对作为因变量的中国在阿富汗的外国直接投资的影响。主要目的是了解GDP增长、人口、通货膨胀、腐败控制、政府效率、政治稳定、利率和失业率是如何相互作用并影响中国在阿富汗的外国直接投资的。
1.Chapter One:Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)refers to the investment made by a companyor individual from one country into a business or entity located in another country.FDI plays a crucial role in the global economy,promoting economic growth,jobcreation,and technology transfer.It involves long-term investments and asignificant degree of control or influence by the investing entity in the hostcountry's operations.In the contemporary landscape of international relations andglobal economics,foreign direct investment(FDI)has emerged as a pivotalinstrument for countries to extend their influence and stimulate economic growth(Pashtoon,2017).One region that has increasingly captured the attention ofinternational investors,particularly China,is Afghanistan.Against the backdrop ofits geopolitical significance,untapped natural resources and strategic goods,andits position within the Belt and Road Initiative(BRI),China's FDI in Afghanistanhas evolved into a subject of paramount importance due to Afghanistan'sattractiveness to China’s FDI and Afghanistan’s need for economic development.
投资分析论文怎么写
.......................
1.2 Problem Statement
While the factors attracting China’s Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)intoAfghanistan hold significant importance,especially in the context of China's Beltand Road Initiative,Afghanistan's strategic location,its rich natural resources,andthe current economic and political climate,there exists a substantial research gapspecifically addressing the factors influencing China’s FDI flow into Afghanistan.Critical questions remain under-explored:What are the driving factors behindChina's FDI in Afghanistan during the period of 2005 to 2022?How do economic,demographic,and political variables influence these investment flows?
Moreover,existing research on the determinants of FDI inflows has largelyconcentrated on both developed and developing countries,overlooking nations likeAfghanistan that are categorized as least developed according to the UnitedNations.The majority of global FDI is channeled towards wealthy,advanced,oremerging economies,leading to a dearth of investment and research focus on least-developed countries.Existing studies on FDI in Afghanistan have primarilyemployed qualitative methodologies or quantitative approaches with limitedvariable scope,lacking comprehensiveness and depth.Additionally,there is anabsence of time series analysis examining the specific factors determining China’sFDI in Afghanistan.
This research aims to fill this gap by focusing on the period from 2005 to2022,exploring the factors that are influencing Chinese investors in Afghanistan,whether they are economic,political,or geopolitical.The study intends to enrichthe existing literature by providing a detailed and comprehensive examination ofthe determinants attracting China’s FDI to Afghanistan,a nation classified as leastdeveloped.It seeks to unravel the complex dimensions influencing China's FDI inAfghanistan,dissecting the trends,motivations,strategies,challenges,andopportunities of this engagement from 2005 to 2022.This study is not only criticalin bridging the existing research gap but also contributes significantly to theacademic literature by providing insights into the multifaceted aspects of China'sFDI in one of the world's least developed countries.
..........................
2.Chapter Two:Literature Review
2.1 Definition of Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)
Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)is an international business activity in whichan individual,a company,or a government entity from one country invests capital,resources,or assets directly into a business or project located in another country.FDI implies a significant degree of ownership,control,and influence by theinvesting entity in the foreign enterprise.It typically involves a long-termcommitment with the aim of establishing lasting interest in the host country(Kakar&Wani,2016).
2.1.1 Forms and Types of FDI that a Chinese Investor Adopts
FDI can take various forms,with the primary distinction being based on thelevel of ownership and control:
Greenfield Investment refers to the establishment of a entirely new businessor operational facility by an investor in a foreign country.In this approach,theinvestor typically initiates the construction of new infrastructure,facilities,andoperational systems from the ground up.This strategy enables the investor to havefull control over the design,operation,and management of the project.Whilegreenfield investments can be resource-intensive and time-consuming,they offerthe advantage of tailoring the project to specific needs and market conditions,often leading to long-term benefits and a greater degree of flexibility compared toacquiring existing businesses or assets in the foreign market(Kakar&Wani,2016).
................
2.2 Motivation for FDI
Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)is a strategic decision undertaken bybusinesses and governments to engage in economic activities in foreign countries.The motivations behind FDI are diverse and reflect a range of economic,strategic,and business considerations.Understanding these motivations is crucial forinvestors and policymakers alike.Here are some key motivations for FDI:Themotivations behind foreign direct investment can vary significantly and include thefollowing:
Market Expansion is a primary driver of Foreign Direct Investment(FDI).Companies pursue FDI to access new markets and customer bases abroad,enabling the sale of their products or services in foreign countries.This strategicmove helps diversify revenue streams and tap into potential growth opportunitieswhen domestic markets become saturated or limited in growth potential(Eryigit&Shafaq,2021).By establishing a presence in foreign markets,companies can tailortheir offerings to local preferences and capitalize on global demand,ultimatelyexpanding their market reach and enhancing competitiveness in the globalbusiness landscape.
Resource Access is a significant motivation for Foreign Direct Investment(FDI).Investors seek FDI opportunities in foreign countries to secure access tocritical resources that may be scarce or economically advantageous in the host nation.These resources include raw materials,energy sources,or a skilled laborforce.By establishing operations in regions abundant in these resources,companies can reduce production costs,improve supply chain stability,and gain acompetitive edge.FDI for resource access ensures a reliable and cost-effectivesupply of essential inputs,contributing to increased efficiency and profitability in aglobal business context.
...........................
3.CHAPTER THREE:METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY...............................35
3.1 INTRODUCTION..................................35
3.2 VARIABLES OF STUDY..........................35
4.CHAPTER FOUR:RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS............................41
4.1 INTRODUCTION.................................41
4.2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS........................................41
5.CHAPTER FIVE:CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATIONS..................51
5.1 CONCLUSION....................................51
5.2 IMPLICATIONS.........................................52
4.Chapter Four:Results and Discussions
4.1 Introduction
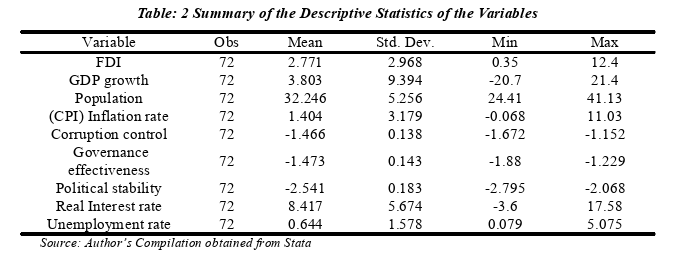
This chapter presents empirical data as well as an analysis of the variablesstudied.The findings of the descriptive statistics and the correlation matrixpresented first and the followed by the findings of Auto-regressive Distributed LagShort-Run Model.
投资分析论文参考
......................
5.Chapter Five:Conclusion andImplications
5.1 Conclusion
This thesis embarked on a comprehensive examination of the factorsinfluencing China's Foreign Direct Investment(FDI)in Afghanistan,employing atime series analysis from 2005 to 2022.Through meticulous research employingthe Auto-regressive Distributed Lag(ARDL)model,this study scrutinized theimpact of various economic,demographic,political,and institutional variables onChina’s FDI in Afghanistan.The findings illuminate the complex interplaybetween these factors and their implications for both China and Afghanistan,aswell as for the broader region involved in these investment dynamics.
The empirical analysis highlighted significant variables affecting China's FDIin Afghanistan.Notably,GDP growth emerged as a pivotal factor,with its positivecorrelation underscoring the attractiveness of Afghanistan's economic environmentto Chinese investors.Conversely,variables such as population size and inflationrate showed no significant impact,suggesting that market size and economicstability,as indicated by inflation,might not be primary considerations for Chineseinvestors under the current economic and political circumstances in Afghanistan.
Interestingly,the study revealed nuanced insights into the role of governanceand political factors.While political stability did not exhibit a statisticallysignificant impact on FDI,the negative coefficients associated with corruptioncontrol and government effectiveness suggest that overly stringent governancemeasures might initially deter investment,despite potentially fostering a morefavorable investment climate over time.
reference(omitted)


